Network monitoring on Linux
This post mentions some linux command line tools that can be used to monitor the network usage. These tools monitor the traffic flowing through network interfaces and measure the speed at which data is currently being transferred. Incoming and outgoing traffic is shown separately.
Some of the commands, show the bandwidth used by individual processes. This makes it easy to detect a process that is overusing network bandwidth.
The tools have different mechanisms of generating the traffic report. Some of the tools like nload read the “/proc/net/dev” file to get traffic stats, whereas some tools use the pcap library to capture all packets and then calculate the total size to estimate the traffic load.
Here is a list of the commands, sorted by their features.
1. Overall bandwidth - nload, bmon, slurm, bwm-ng, cbm, speedometer, netload
2. Overall bandwidth (batch style output) - vnstat, ifstat, dstat, collectl
2. Bandwidth per socket connection - iftop, iptraf, tcptrack, pktstat, netwatch, trafshow
3. Bandwidth per process - nethogs
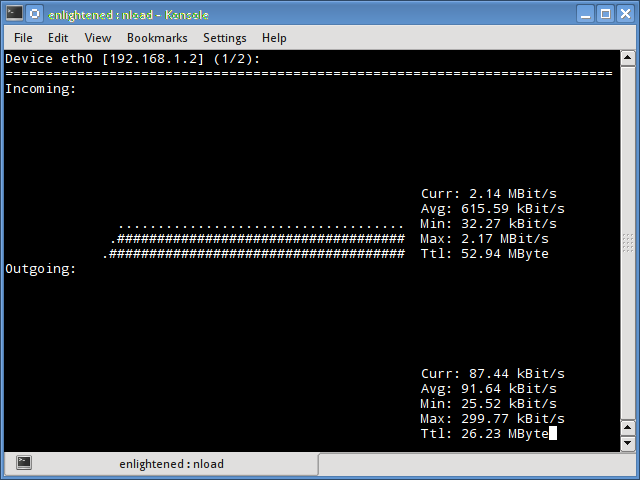
1. Nload
Nload is a commandline tool that allows users to monitor the incoming and outgoing traffic separately. It also draws out a graph to indicate the same, the scale of which can be adjusted. Easy and simple to use, and does not support many options.
So if you just need to take a quick look at the total bandwidth usage without details of individual processes, then nload will be handy.
$ nload
Installing Nload – Fedora and Ubuntu have got it in the default repos. CentOS users need to get nload from Epel repositories.
# fedora or centos
$ yum install nload -y
# ubuntu/debian
$ sudo apt-get install nload
2. iftop
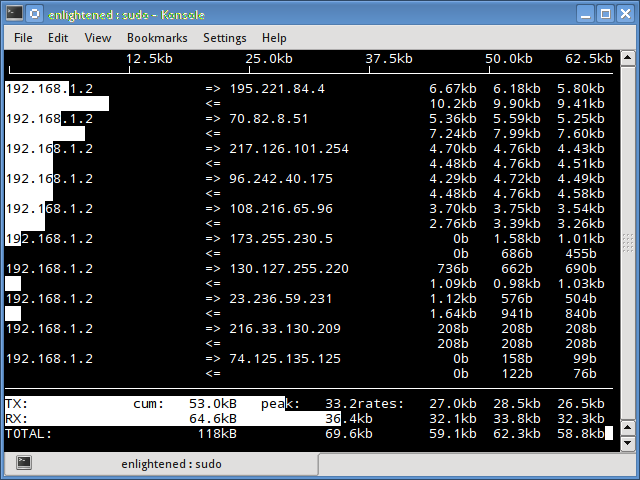
Iftop measures the data flowing through individual socket connections, and it works in a manner that is different from Nload. Iftop uses the pcap library to capture the packets moving in and out of the network adapter, and then sums up the size and count to find the total bandwidth under use.
Although iftop reports the bandwidth used by individual connections, it cannot report the process name/id involved in the particular socket connection. But being based on the pcap library, iftop is able to filter the traffic and report bandwidth usage over selected host connections as specified by the filter.
$ sudo iftop -n
The n option prevents iftop from resolving ip addresses to hostname, which causes additional network traffic of its own.
Install iftop – Ubuntu/Debian/Fedora users get it from default repos. CentOS users get it from Epel.
# fedora or centos
yum install iftop -y
# ubuntu or debian
$ sudo apt-get install iftop
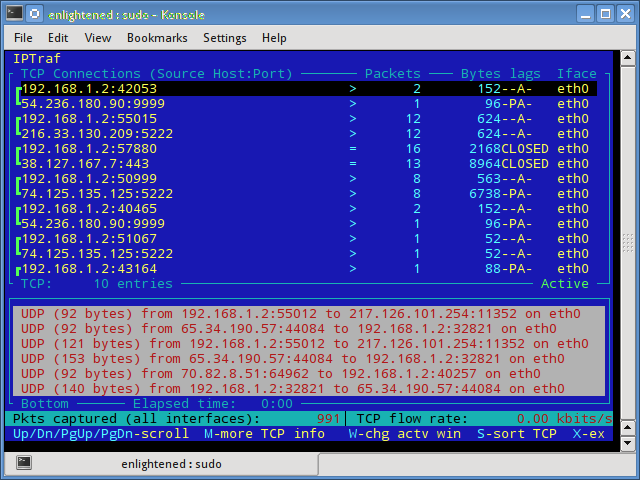
3. iptraf
Iptraf is an interactive and colorful IP Lan monitor. It shows individual connections and the amount of data flowing between the hosts. Here is a screenshot.
$ sudo iptraf
Install iptraf
# Centos (base repo)
$ yum install iptraf
# fedora or centos (with epel)
$ yum install iptraf-ng -y
# ubuntu or debian
$ sudo apt-get install iptraf iptraf-ng
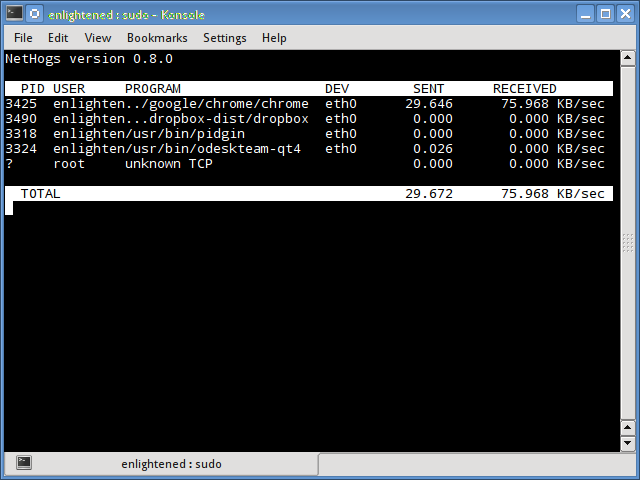
4. nethogs
Nethogs is a small ‘net top’ tool that shows the bandwidth used by individual processes and sorts the list putting the most intensive processes on top. In the event of a sudden bandwidth spike, quickly open nethogs and find the process responsible. Nethogs reports the PID, user and the path of the program.
$ sudo nethogs
4. nethogs
Nethogs is a small ‘net top’ tool that shows the bandwidth used by individual processes and sorts the list putting the most intensive processes on top. In the event of a sudden bandwidth spike, quickly open nethogs and find the process responsible. Nethogs reports the PID, user and the path of the program.
$ sudo nethogs
Install Nethogs – Ubuntu, Debian, Fedora users get from default repos. CentOS users need Epel
# ubuntu or debian (default repos)
$ sudo apt-get install nethogs
# fedora or centos (from epel)
$ sudo yum install nethogs -y
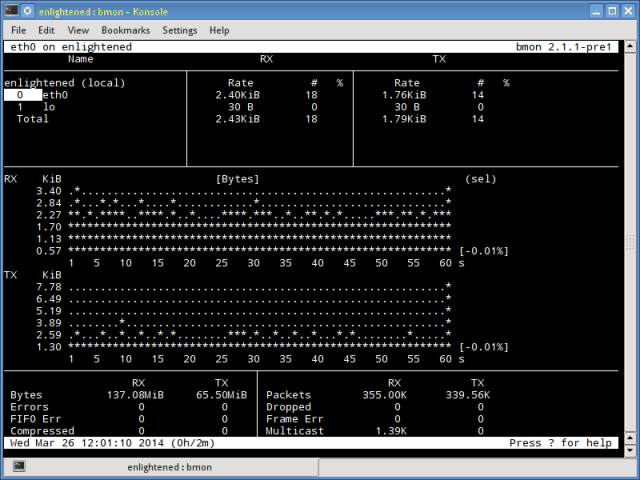
5. bmon
Bmon (Bandwidth Monitor) is a tool similar to nload that shows the traffic load over all the network interfaces on the system. The output also consists of a graph and a section with packet level details.
Install Bmon – Ubuntu, Debian and Fedora users can install from default repos. CentOS users need to setup repoforge, since its not available in Epel.
# ubuntu or debian
$ sudo apt-get install bmon
# fedora or centos (from repoforge)
$ sudo yum install bmon
Bmon supports many options and is capable of producing reports in html format. Check the man page for more information
6. slurm
Slurm is ‘yet’ another network load monitor that shows device statistics along with an ascii graph. It supports 3 different styles of graphs each of which can be activated using the c, s and l keys. Simple in features, slurm does not display any further details about the network load.
$ slurm -s -i eth0
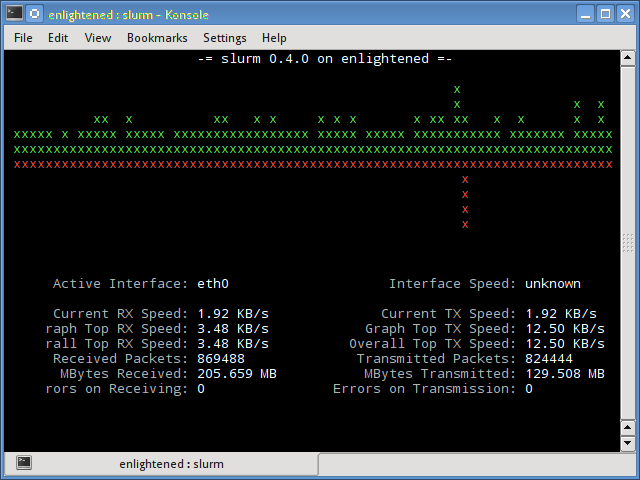
Install slurm
# debian or ubuntu
$ sudo apt-get install slurm
# fedora or centos
$ sudo yum install slurm -y
7. tcptrack
Tcptrack is similar to iftop, and uses the pcap library to capture packets and calculate various statistics like the bandwidth used in each connection. It also supports the standard pcap filters that can be used to monitor specific connections.
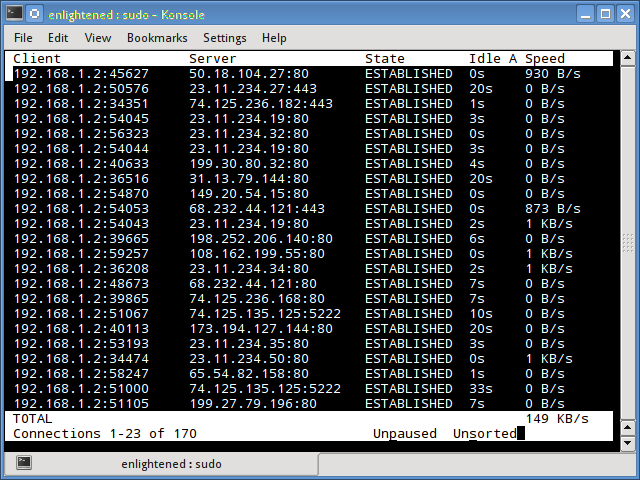
Install tcptrack – Ubuntu, Debian and Fedora have it in default repos. CentOS users need to get it from RepoForge as it is not available in Epel either.
# ubuntu, debian
$ sudo apt-get install tcptrack
# fedora, centos (from repoforge repository)
$ sudo yum install tcptrack
8. Vnstat
Vnstat is bit different from most of the other tools. It actually runs a background service/daemon and keeps recording the size of data transfer all the time. Next it can be used to generate a report of the history of network usage.
$ service vnstat status
* vnStat daemon is running
Running vnstat without any options would simply show the total amount of data transfer that took place since the date the daemon is running.
$ vnstat
Database updated: Mon Mar 17 15:26:59 2014
eth0 since 06/12/13
rx: 135.14 GiB tx: 35.76 GiB total: 170.90 GiB
monthly
rx | tx | total | avg. rate
------------------------+-------------+-------------+---------------
Feb '14 8.19 GiB | 2.08 GiB | 10.27 GiB | 35.60 kbit/s
Mar '14 4.98 GiB | 1.52 GiB | 6.50 GiB | 37.93 kbit/s
------------------------+-------------+-------------+---------------
estimated 9.28 GiB | 2.83 GiB | 12.11 GiB |
daily
rx | tx | total | avg. rate
------------------------+-------------+-------------+---------------
yesterday 236.11 MiB | 98.61 MiB | 334.72 MiB | 31.74 kbit/s
today 128.55 MiB | 41.00 MiB | 169.56 MiB | 24.97 kbit/s
------------------------+-------------+-------------+---------------
estimated 199 MiB | 63 MiB | 262 MiB |
To monitor the bandwidth usage in realtime, use the ‘-l’ option (live mode). It would then show the total bandwidth used by incoming and outgoing data, but in a very precise manner without any internal details about host connections or processes.
$ vnstat -l -i eth0
Monitoring eth0... (press CTRL-C to stop)
rx: 12 kbit/s 10 p/s tx: 12 kbit/s 11 p/s
Vnstat is more like a tool to get historic reports of how much bandwidth is used everyday or over the past month. It is not strictly a tool for monitoring the network in real time.
Vnstat supports many options, details about which can be found in the man page.
Install vnstat
# ubuntu or debian
$ sudo apt-get install vnstat
# fedora or centos (from epel)
$ sudo yum install vnstat
9. bwm-ng
Bwm-ng (Bandwidth Monitor Next Generation) is another very simple real time network load monitor that reports a summary of the speed at which data is being transferred in and out of all available network interfaces on the system.
$ bwm-ng
bwm-ng v0.6 (probing every 0.500s), press 'h' for help
input: /proc/net/dev type: rate
/ iface Rx Tx T
ot==========================================================================
== eth0: 0.53 KB/s 1.31 KB/s 1.84
KB lo: 0.00 KB/s 0.00 KB/s 0.00
KB--------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- total: 0.53 KB/s 1.31 KB/s 1.84
KB/s
If the console size is sufficiently large, bwm-ng can also draw bar graphs for the traffic using the curses2 output mode.
$ bwm-ng -o curses2
Install Bwm-NG – On CentOS bwm-ng can be installed from Epel.
# ubuntu or debian
$ sudo apt-get install bwm-ng
# fedora or centos (from epel)
$ sudo apt-get install bwm-ng
10. cbm – Color Bandwidth Meter
A tiny little simple bandwidth monitor that displays the traffic volume through network interfaces. No further options, just the traffic stats are display and updated in realtime.
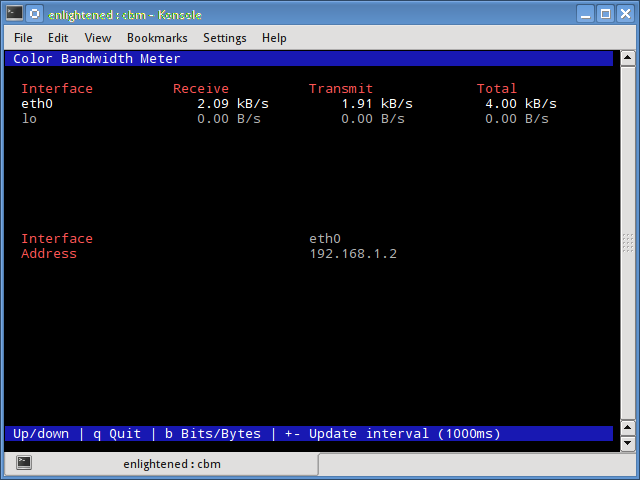
$ sudo apt-get install cbm
11. speedometer
Another small and simple tool that just draws out good looking graphs of incoming and outgoing traffic through a given interface.
$ speedometer -r eth0 -t eth0
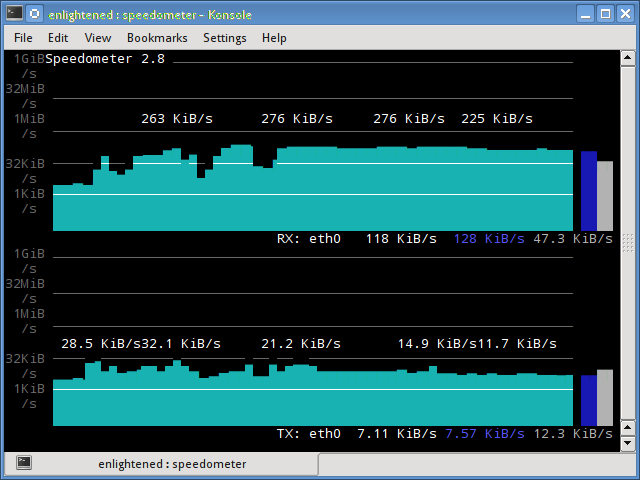
Install speedometer
# ubuntu or debian users
$ sudo apt-get install speedometer
12. Pktstat
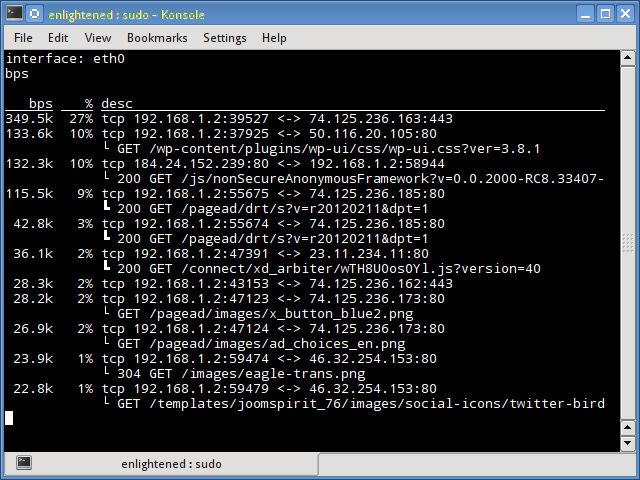
Pktstat displays all the active connections in real time, and the speed at which data is being transferred through them. It also displays the type of the connection, i.e. tcp or udp and also details about http requests if involved.
$ sudo pktstat -i eth0 -nt
$ sudo apt-get install pktstat
13. Netwatch
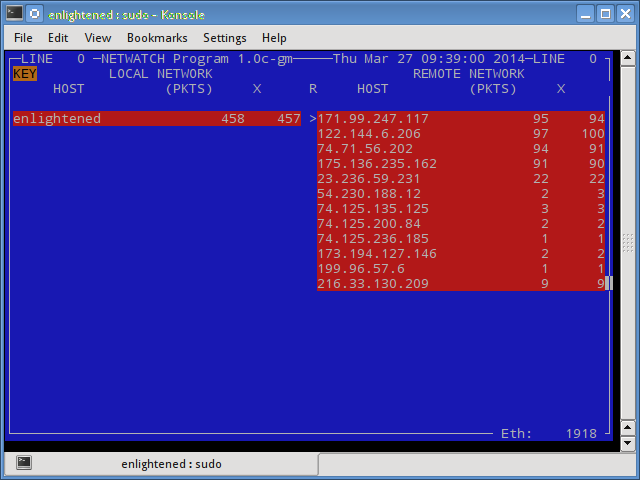
Netwatch is part of the netdiag collection of tools, and it too displays the connections between local host and other remote hosts, and the speed at which data is transferring on each connection.
$ sudo netwatch -e eth0 -nt
$ sudo apt-get install netdiag
14. Trafshow
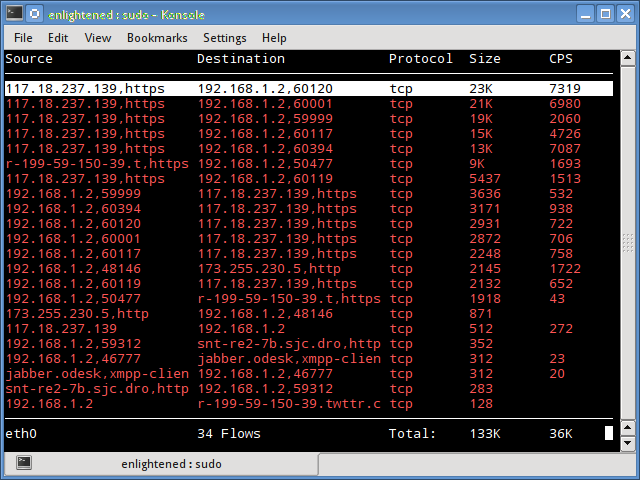
Like netwatch and pktstat, trafshow reports the current active connections, their protocol and the data transfer speed on each connection. It can filter out connections using pcap type filters.
Monitor only tcp connections
$ sudo trafshow -i eth0 tcp
$ sudo apt-get install netdiag
15. Netload
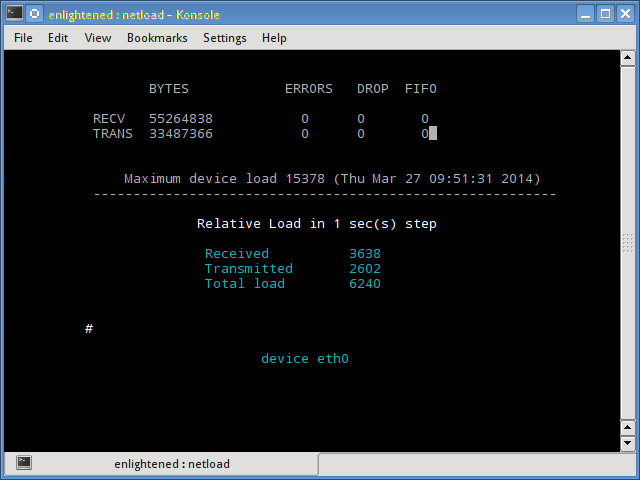
The netload command just displays a small report on the current traffic load, and the total number of bytes transferred since the program start. No more features are there. Its part of the netdiag.
$ netload eth0
$ sudo apt-get install netdiag
16. ifstat
The ifstat reports the network bandwidth in a batch style mode. The output is in a format that is easy to log and parse using other programs or utilities.
$ ifstat -t -i eth0 0.5
Time eth0
HH:MM:SS KB/s in KB/s out
09:59:21 2.62 2.80
09:59:22 2.10 1.78
09:59:22 2.67 1.84
09:59:23 2.06 1.98
09:59:23 1.73 1.79
Install ifstat – Ubuntu, Debian and Fedora users have it in the default repos. CentOS users need to get it from Repoforge, since its not there in Epel.
# ubuntu, debian
$ sudo apt-get install ifstat
# fedora, centos (Repoforge)
$ sudo yum install ifstat
17. dstat
Dstat is a versatile tool (written in python) that can monitor different system statistics and report them in a batch style mode or log the data to a csv or similar file. This example shows how to use dstat to report network bandwidth
$ dstat -nt
-net/total- ----system----
recv send| time
0 0 |23-03 10:27:13
1738B 1810B|23-03 10:27:14
2937B 2610B|23-03 10:27:15
2319B 2232B|23-03 10:27:16
2738B 2508B|23-03 10:27:17
Install dstat
$ sudo apt-get install dstat
18. collectl
Collectl reports system statistics in a style that is similar to dstat, and like dstat it is gathers statistics about various different system resources like cpu, memory, network etc. Over here is a simple example of how to use it to report network usage/bandwidth.
$ collectl -sn -oT -i0.5
waiting for 0.5 second sample...
# <----------Network---------->
#Time KBIn PktIn KBOut PktOut
10:32:01 40 58 43 66
10:32:01 27 58 3 32
10:32:02 3 28 9 44
10:32:02 5 42 96 96
10:32:03 5 48 3 28
Install Collectl
# Ubuntu/Debian users
$ sudo apt-get install collectl
#Fedora
$ sudo yum install collectl
Summary
Those were a few handy commands to quickly check the network bandwidth on your linux server. However these need the user to login to the remote server over ssh. Alternatively web based monitoring tools can also be used for the same task.
Ntop and Darkstat are some of the basic web based network monitoring tools available for Linux. Beyond these lie the enterprise level monitoring tools like Nagios that provide a host of features to not just monitor a server but entire infrastructure.
source:http://www.binarytides.com/linux-commands-monitor-network/